Partial Double Bond Character of Peptide Bond
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Partial double bonds are caused by resonance in a structure which is the transfer of π electrons those which form the second bond in a double bond from one site to another.
Start studying Topic 1 - Peptide Bonds.
. Answer 1 of 5. Partial double bond character estimated at 40 under typical conditions The from BIOL 12 at University of Virginia. The evidence that shows this partial double bond character is from the length of the bond.
Partial double bonds are caused by resonance in a structure which is the transfer of π electrons those which form the second bond in a double bond from one site to another. A partial pi bond can also cause a partial triple bond. The partial double bond character of peptide bond prevent free rotation of polypeptide chain.
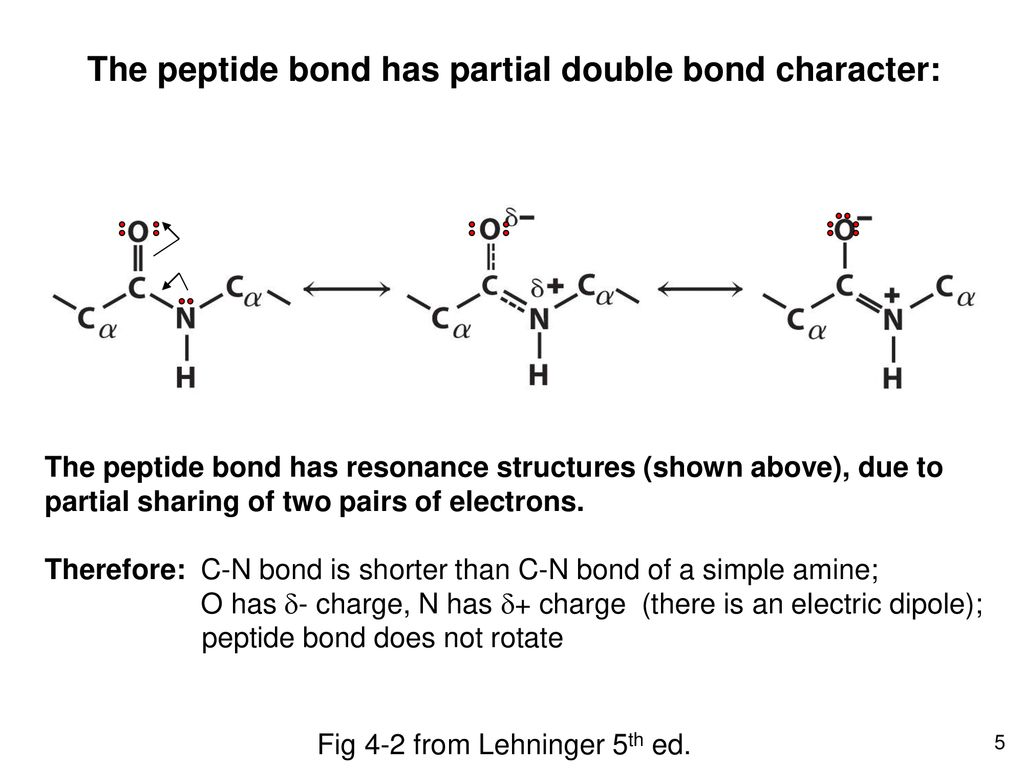
One solid line and one dashed line. The peptide bond is rigid and planar with a partial double bond in character. Formation of the peptide bond is a condensation reactionspecifically a dehydration reaction involving the loss of waternot a hydration reaction involving the addition of water.
It is shorter than a single bond and is therefore rigid and planar. Study sets textbooks questions. Chemistry questions and answers.
This prevents free rotation around the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen of the peptide bond. Resonance Structure of Peptide Bond. The peptide bond is trans It never occurs in cis configuration due to steric hindrance.
The partial double-bond character of the bond that links the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen of a peptide renders four atoms of the peptide bond coplanar and restricts the number of possible peptide conformations. A peptide bond O C. A partial double bond is indicated with two parallel lines like a normal double bond.
The carbonyl oxygen has a partial negative -028 charge and is a good hydrogen bond acceptor while the amide nitrogen is partially positive 028 and a good hydrogen bond donor. A partial triple bond has a bond order between 2 and 3. Thus peptide bond attains a planar geometry and sp 2 hybridisation.
A Bulky side chains prevent free rotation around the bond. Peptide bond possesses a partial double bond character of C-N bond due to delocalisation of unshared pair of electrons coming from nitrogen into the carbonyl group CO. An ionic bond O D.
Significant delocalisation of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom gives the group a partial double bond character. The peptide bond has a partial double-bond character- that is. Answer 1 of 3.
The partial double bond renders the amide group planar occurring in either the cis or trans isomers. A disulfide bond OB. Thus the peptide bond has a partial double bond character and exhibits limited rotation eliminating choice C.
The short carbonyl carbonnitrogen bond length 0132 nm the usual carbonnitrogen single bond length is 0147 nm is consistent with the partial double-bond character of the peptide linkage. B It exhibits partial double-bond character preventing rotation. While drawn as a single bond the peptide bond has partial double bond character that enforces a well-defined flat structure.
In the diagram of a peptide shown which bonds are not free to rotate due to the partial double bond character. The rigid planar nature of the peptide unit has. Generally speaking peptide bonds are in the trans conformation.
The amide structure has two resonance contributors. Both CO and NH groups of peptide bonds are planar and are involved in hydrogen bond formation. By process of elimination choice D is false.
In the unfolded state of proteins the peptide groups are free to isomerize and adopt both isomers. D None of the above. Why is the peptide bond planar.
A hydrogen bond Shown here is phenylalanine with the carboxyl group in red and the amino group in blue. Peptide bond is rigid and planner. Thus the peptide unit is a planar rigid structure and rotation in the peptide backbone is restricted to the bonds involving the a carbon.
Thus the partial double bond character of CN in the peptide group means that this bond is shorter than would be predicted for a CN single bond whilst the CO bond having a partial single bond character due to resonance is longer than would be predicted for a CO double bond. The reason they are partial is because the structure can. Peptide bond has partial double bond character so it is shorter than single bond and longer than double bond.
They are listed above1. Part 1 1 point Of all the different bond types found in proteins which has partial double bond character. Lack of rotation around the bond.
However in the folded state only a single isomer is adopted. Partial double bond character. There are about three major characteristics of a peptide bond.
E All of the above. It generally exists in trans-configuration. It is 013 Angstrom shorter than the.
Because the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen has a partial double bond character rotation around this bond is restricted. The planarity and rigidity of the peptide bond are accounted for by the fact that free rotation cannot occur around double bonds. A partial double bond has a bond order between one and 2.
The peptide bond is a stable covalent bond and is said to be a rigid planar bond because it has a partial double bond character. C Hydrogen bonding between the NH and CO groups limits movement.
Read The Following Slides By Day 12 Ppt Download

Structural Biochemistry Organic Chemistry Important Organic Reactions In Biochemistry Peptide Bonding Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
No comments for "Partial Double Bond Character of Peptide Bond"
Post a Comment